In the U.S. global retail sales of plant-based meat, seafood, milk, yogurt, ice cream, and cheese totaled $8.1 billion in 2024, doubling its 2017 values. These categories represent over a quarter of global plant-based retail sales, which recently reached $28.6 billion, according to a recent report from industry group The Good Food Institute.
The 2024 State of Alternative Proteins constitutes a series of reports across plant-based categories, including cultivated ingredients, fermentation-derived plant-based analogs, traditional plant-based substitutes, and investment opportunities in the sector. Report insight reveals that now is a great time to be in the plant-based sector, as its gaining share as a global movement with opportunities across myriad markets.
Globally, for example, plant-based sales are up roughly 5% despite one of the largest market leaders, the U.S. market, stagnating somewhat. Domestically, GFI anticipates a rebound following several auspicious events.
“While the impact of high inflation played out in the market and consumers expressed widespread frustration around grocery costs, positive signs for the plant-based sector emerged in 2024, including innovative new product launches, a growing demand for plant-based eggs, and improved velocities (how fast items are turning over at shelf) across several plant-based categories,” read the report.
Plant-Based Analogs
In addition to record sales, collaboration heated up in 2024, with at least 13 partnerships formed in the sector, centering around product. development and technology. Additionally, major players dialed in their operations capabilities with the formation of 26 plant-based facilities that were either announced or developed throughout the year.
In the global context, North America is the third-largest consumer of plant-based foods by sales, trailed by Europe and the Asia Pacific regions.
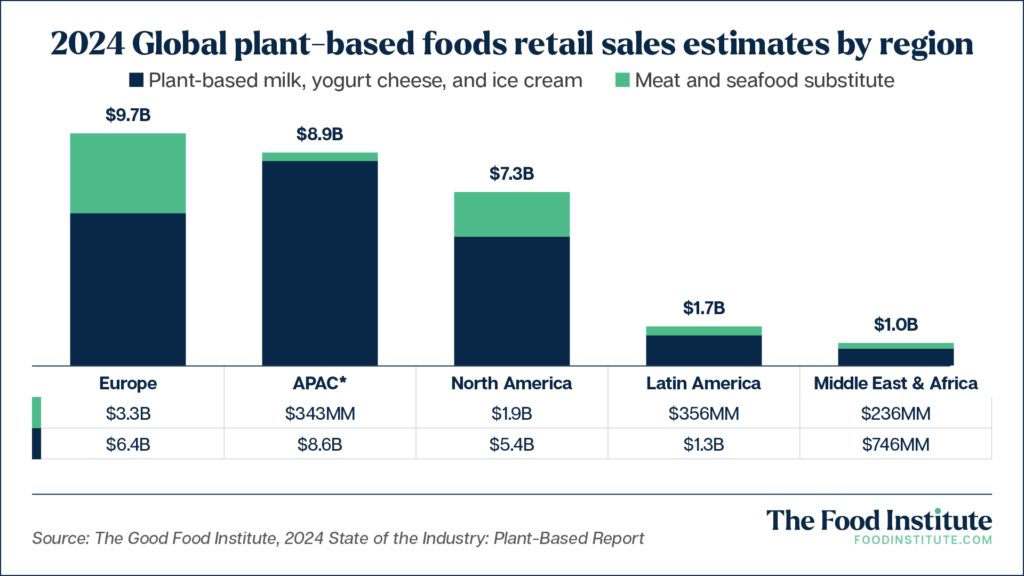
The report highlighted that global sales for the retail plant-based meat and seafood sector were up 4% from 2023, while retail plant-based sales for dairy accelerated even more, up 5% compared to the year before.
This data shows the U.S.’s domestic stagnation to be the exception rather than the rule: between 2023-24, dollar sales were down 4% (reaching $8.08 billion by YE), while unit sales dropped 5% (reaching 1.7 billion by YE). The report, however, noted that pockets of growth mitigated declines through product launches and reformulations to better address consumer needs.
Some growth pockets by unit velocities include plant-based protein liquids and powders (+13% between 2023-24); plant-based baked goods and other desserts (+13%); and tofu, tempeh, and seitan (+6%). These offerings likely benefited from increased interest in personal health and well-being and the desire for macro-nutrient-packed convenience.
Moreover, academic research and patents reveal that plant-based will be here to stay for years to come. Research articles that discuss plant-based, hybrid, and blended alternatives reached 825 in 2024 from 649 the year before, while cumulative patent families for meat and dairy analogs exceeded 1,200 last year.
Cultivated Meat, Seafood, Ingredients
Cultivated or lab-grown meat refers to a process wherein meat is created by culturing the cells in a bioreactor through precision fermentation (similar to some cheese-making methods). The animal cells are sourced from a live animal and does not require an animal to be slaughtered in the process.
After receiving approval from the FDA and USDA to merchandise cultivated meat in the U.S., a suite of state-level anti-cultivation legislation has taken hold in various states.
Most recently, Nebraska and Indiana received final approval in mid-May to ban the distribution and sale of these offerings, following lockstep with bills from Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, and Montana.
These initiatives have undoubtedly stymied the innovation’s progress and public perception in the U.S. Nevertheless, the products can also be sold in Singapore, and markets such as Israel have made moves to approve these products in 2024.
“Like many transformative innovations in their early days, cultivated meat faces a set of difficult–if predictable–challenges: early-stage funding constraints, technical and cost hurdles, and lack of clarity around regulatory timelines, to name a few,” read the report.
This hasn’t stopped major retailers from investing in cultivated products. Cargill, Coca-Cola, Danone, JBS, Maple Leaf, Nestlé, and Tyson, for example, have made moves in recent years to increase their market share in these potentially transformative offerings.
Evidence suggests that U.S. consumers are gradually warming up to these products. A survey of 2,214 U.S. adults from Morning Consult found that 32% found cultivated meats to be somewhat/very appealing, 28% were at least very likely to try a free sample, and 17% were at least very likely to purchase a product made using the process if able.
Abroad, a similar report found that more than 50% of consumers in various European countries would be willing to try the offering, including in Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain.
The Food Institute Podcast
It’s tariff time, and companies the world over are working to better understand how their operations will be impacted. Jodi Ader from RSM US LLP joined The Food Institute Podcast to discuss which products and inputs are currently subject to tariffs, and how to best mitigate supply chain risks.












